DIVING WITH WHALE SHARKS
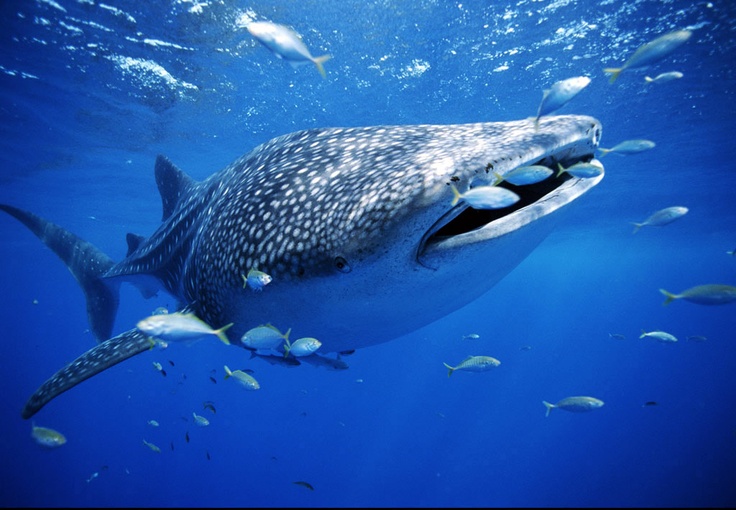



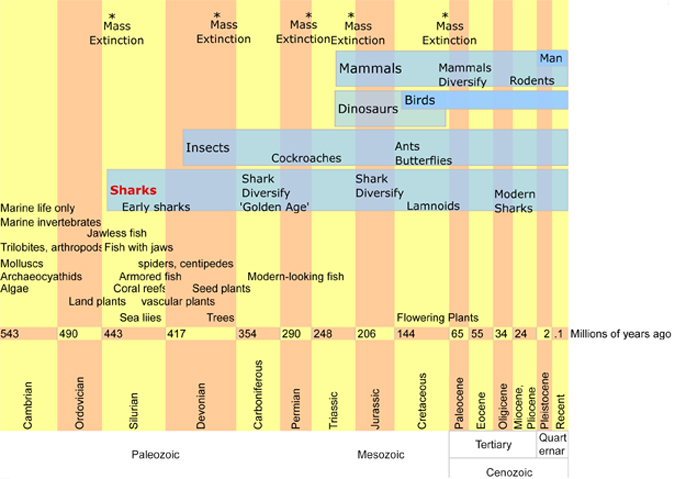
Whale Sharks, Rhyncodon typus, are the largest cartilaginous fish in the world today. The largest ever recorded was just over 41ft long, but rumors by fishermen say that they may grow over 46ft in length which makes whale sharks the second largest cartilaginous fish ever to exist and places them only second in length next to the Megalodon shark that existed some 20 million years ago and as recently as 1.6 million years ago. Only true mammalian whales are greater in length than whale sharks, with the blue whale being the largest creature by mass to ever exist on this planet. Like some species of whales, the whale shark has been able to achieve it’s great size by eating the smallest food source; plankton. They also eat krill, small fish, jellyfish, and squid. Whale sharks are one of only three types of sharks that through convergent evolution some 60 to 30 years ago became plankton feeders. The other two plankton feeders are both lamnoid sharks and include the megamouth shark and the basking shark. These two sharks have more in common with great whites than they do with whale sharks.
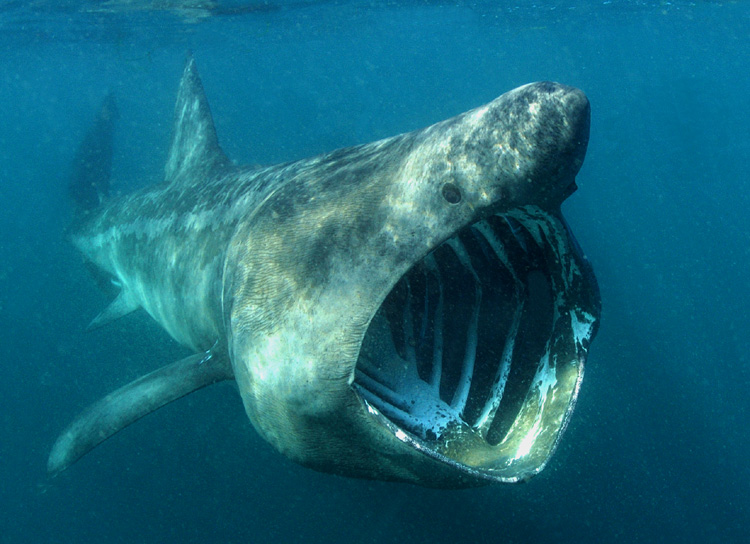
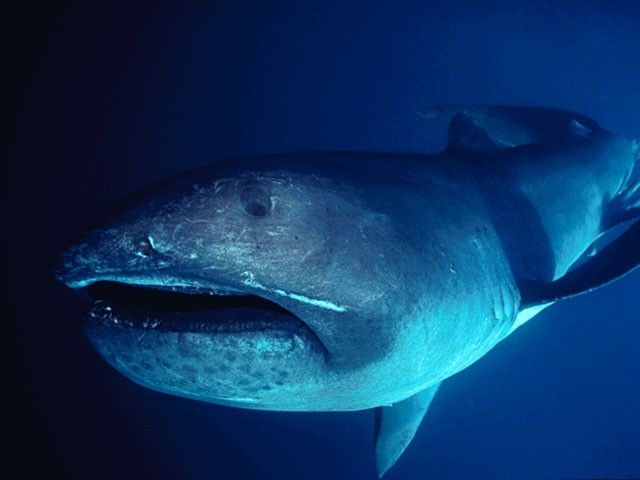


Whale sharks belong to the order Orectolobiformes and are related closer to carpet sharks such as wobbegongs and nurse sharks. Whale sharks have a distinct checkerboard pattern of lines and dots on their top/dorsal side that would be useful for a shark that tended to lay hidden in plain sight on the substrate, but whale sharks are constant movers, so why exactly they retain their bottom dweller camouflage pattern after millions of years is not quite clear. Perhaps the pattern helps diffuse radiation on their skin as they glide so close to the surface. Perhaps it helps distinguish others of their kind from predator sharks such as the now extinct Megalodon sharks and current Great White sharks.
Besides their length and disruptive color patterns, there are several other features that make whale sharks unique. To start with, they swim by not only moving their tail from side to side, but by moving two thirds of their body length from side to side. Only the head region remains relatively stationary as they thrust forward in the water forcing huge volumes of water to flow into their forward facing over one meter (3.3 feet) wide mouth. The seawater is expelled out though their five pairs of gills similar to how giant mantas feed, but on a scale as great as 6,000 liters of water per hour. Any plankton in the water over 1millimeter in size becomes trapped by thousands of 10cm long bristles that make up the gill-rakers and is eventually swallowed and passed down a relatively small digestive tract.
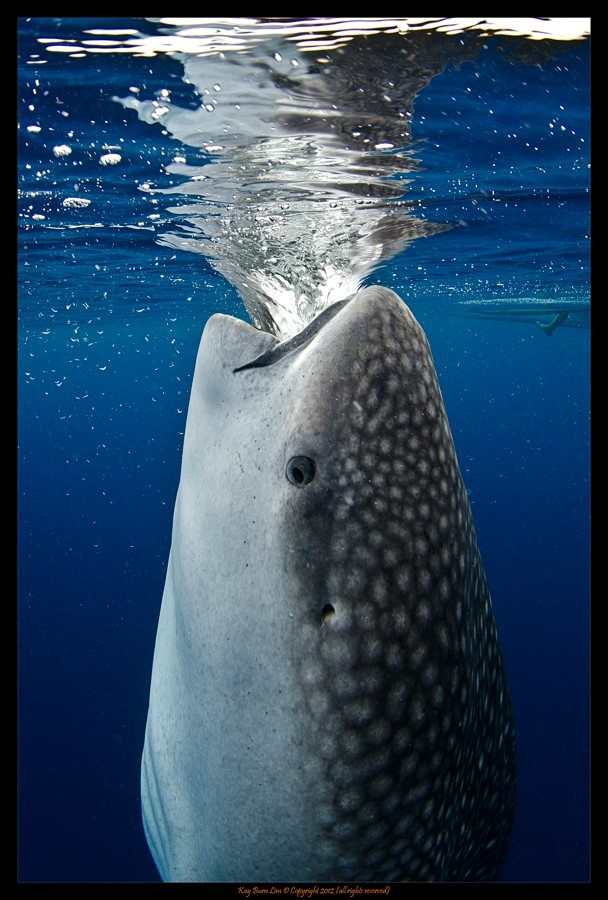
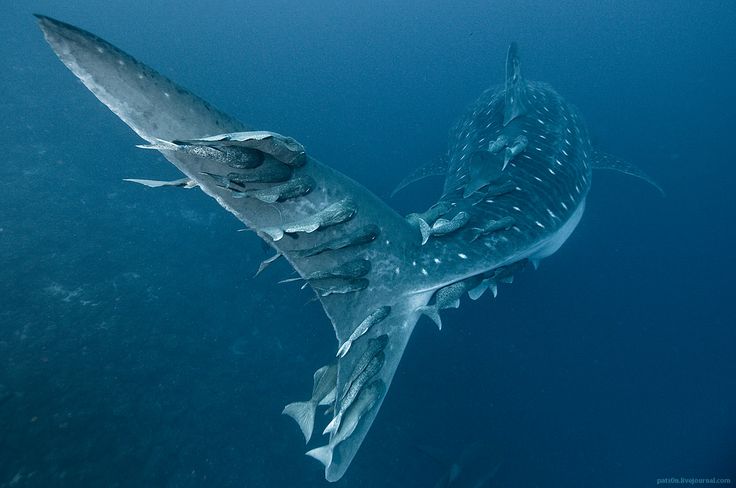


Only modern hammerheads sharks move their entire bodies from side to side as they hunt using the electrical receptors in their head to locate buried fish in the sand like a metal detector passing back and forth for greater coverage. Unlike other plankton feeders, whale sharks can also thrust their jaw forward and suck up plankton or small fish. Inside their mouth are some 300 rows containing over 3000 small slightly hooked Velcro like teeth. These small teeth may be used as a rough raspy surface to make it more difficult for small slippery jellyfish and slick squids to escape their ultimate fate, but little other purpose for these tiny teeth has yet to be documented. We do know that Mother Nature does not like to waste energy, and therefore a species will lose what it doesn’t use. For instance, after a brief 10,000 years living in perpetually dark caves, fish will lose their eyesight and become blind. Over millions of years ancestors of whales that returned to the sea, lost their back legs in addition to other bodily changes. Zygorhiza, a primitive 6m/24ft whale had hand sized back legs, while modern whales show no outward sign of ever having back legs except for possible small internal vestigial remnants of back leg bones.



As for their life span, we believe that they may mature after 30 years and live for over 100 years. One female can carry some 300 encased embryos. Offspring are born live: ovoviviparous. The smallest whale shark ever found was less than .5m/15inches in length. Juveniles have been found in the stomachs of blue sharks and blue marlin to name a few. In Taiwan they are called the tofu shark because of their taste and texture. They are currently determined to be vulnerable as a species, but as more divers and snorklers alike get the opportunity to swim with these gentle giants more may be done to assure their ultimate survival.
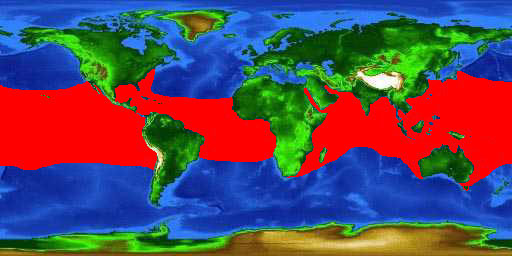
Now once you know how whale sharks live and what they feed on it is easier to find them in the wild. They live in tropical and warm-temperate waters around the world including the Gulf of Mexico, the Yucatan, Belize, Indonesia, the Philippines, Taiwan, Israel, Jordan, Africa, Yap, and anywhere else near the equator or where the water temp is between 70-86 degrees Fahrenheit (21-30ºC). They will also migrate in many other destinations at certain times of the year such as the Galapagos Islands, Andaman Sea, Honduras, Myanmar, Thailand, Sumatra and Indian Ocean. Much of their habitat overlays the habitat of mantas and other plankton feeders. However, whale sharks are not only found on the surface near bays, reefs, or inside lagoons, but they are known to dive down to 1,286m/4,219ft.
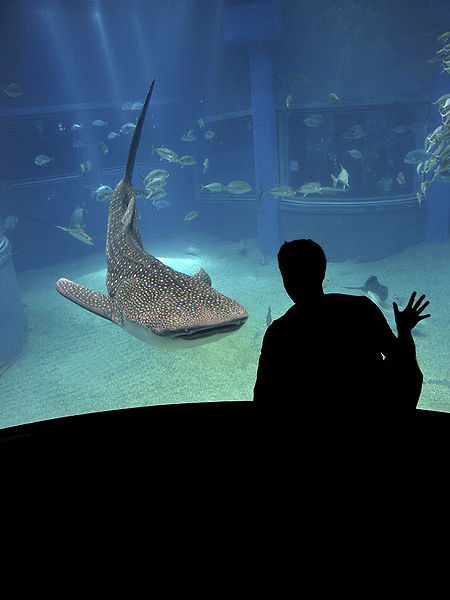
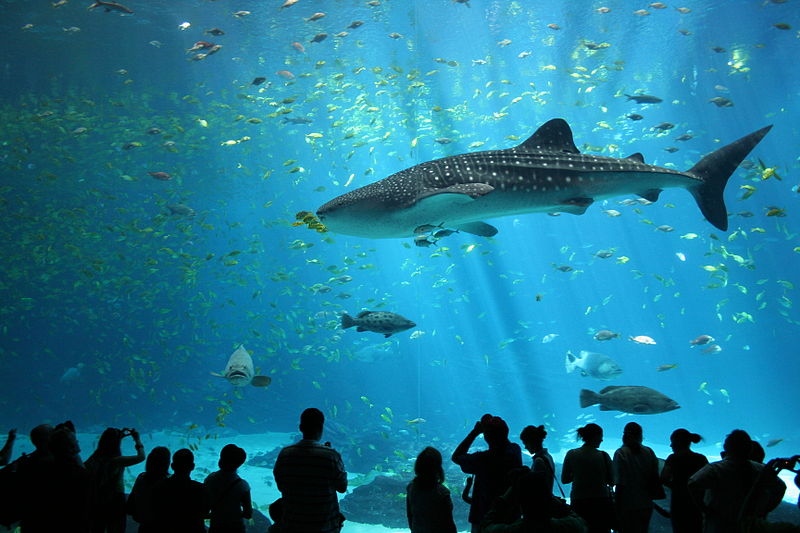



Guides off Isla Mujeres, Mexico to Ningaloo Reef, Australia look for signs of sea birds flocking over the water or tuna jumping in the water. Chances are, the birds and tuna are there to get the fish that have been attracted to the high concentrations of plankton. It won’t take long for one or more whale sharks to join in on the planktonic festivities. Some whale sharks such as a few off of Yap Island, Utila Honduras, and Indonesia like to reside there year round, while others migrate great distances to their preferred feeding destinations. Three days before or after a full moon when corals and reef fish spawn, whale sharks will congregate near these designated areas. In 2011 some 400 whale sharks congregated off the Yucatan coast of Mexico to feast on the aggregate release of cubera, mutton, and dog snapper larvae.
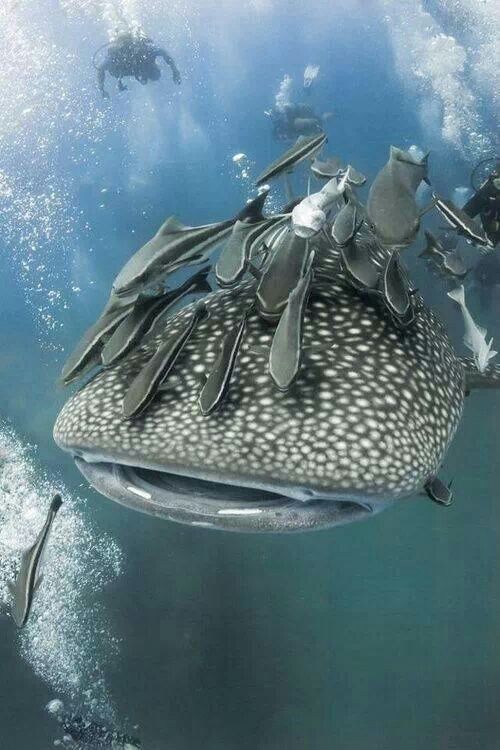
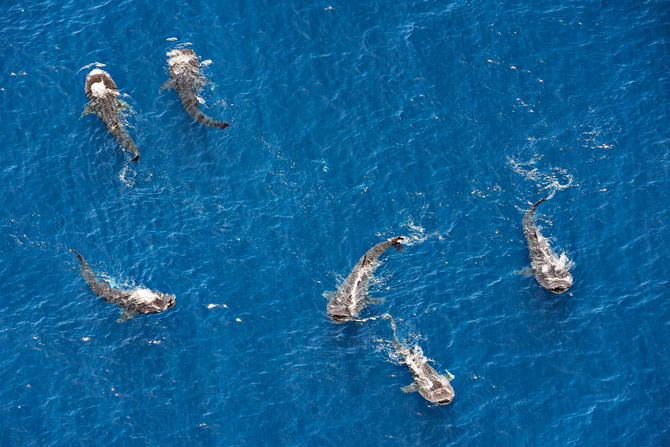



Now you might encounter a whale shark while diving off of Tampa, Florida, an oil rig in the gulf, or off of Costa Rica, but the most popular sites don’t even let you scuba dive with these fish. At certain locations masks and snorkels are permitted only, no flash photography, and keep a distance of 3.3m/10ft away from the fish. Belize is one of the few exceptions, as you may have to scuba dive down to 33m/100ft to view the whale sharks here. The point is that they want the tourists to enjoy the viewing without scaring or harassing the fish. Even a hand on a fin will remove a thin layer of gel that keeps bacteria away from the whale shark’s body, and locals will do anything to protect the tourist equivalent of an aquatic cash cow; if you will.
So when is the best time to see these massive creatures? The locations and time periods vary but here are a few. In Mozambique the best time is November to February, in the Yucatan mid-July to August, at Ningaloo Reef mid March to mid-August, for Belize April to May, Galapagos Islands June to November and in the Philippines December to May with the most whale sharks congregating February to April, but the waters are the calmest April to November. Yeah, sounds a little complicated, and in addition to all this, as famous formidable fish, whale sharks ultimately migrate when they wish.

Recent Posts
- Eastern Malaysia, Sabah, Sipadan & More
- Ghost Pipefish, Pipefish, Seahorses, and Sea Dragons
- Australia Queensland and the Great Barrier Reef
- Tioman Islands, Malaysia
- The Riviera Maya
- The Peter Diving System
- The Bay Islands, Roatan, Utila, Guanaja, and more.
- The Cuttlefish; The Undisputed Master of Camouflage.
- The Maldives: A Garland of Islands in the Indian Ocean
- Frogfish, The Overlooked Camouflage Artist
Categories
- Australia
- Bahamas
- Bay Islands
- Belize
- Blue Hole
- Bonaire Diving
- Borneo
- Cayman Brac
- Cayman Islands
- Cozumel
- Curacao
- Cuttlefish
- Dive Destinations
- Dive Equipment
- Dive Liveaboards
- Dive Resorts / Properties
- Dive Travel
- Dive Travel Deals
- Diver Wellness
- Dolphins
- Dominica
- Eagle Rays
- eagle rays
- Family Travel
- Fiji
- Galapagos Islands
- Great White Shark cage diving
- Guanaja
- Honduras
- Indonesia
- Infographics
- Isla Mujeres
- Learning to Dive
- Little Cayman
- Maduro Dive Newsletter
- Malaysia
- Maldives
- Manta Rays
- Marine Life
- Mexico
- Micronesia
- Muck Diving
- Myamar
- Palau
- Papua New Guinea
- Pelagics
- Philippines
- Pinnacles
- Polynesia
- Reefs
- Riviera Maya
- Roatan
- Saba
- Sabah
- Scuba Diving
- Scuba Gear Reviews
- Scuba News/Events
- Scuba Training & Education
- Sea Legends
- sea lions
- Sea of Cortez
- Sharks
- Single Travel
- Sipadan
- Socorro Islands
- South Africa
- Specialties
- ST. Kitts
- Stingrays
- Tahiti
- Thailand
- The Bucket List
- Tobago
- Truk Lagoon (Chuuk)
- Turks and Caicos Islands
- Turtles
- Uncategorized
- Underwater Photography
- Underwater Video
- Utila
- Walls
- Whale Sharks
- Whales
- Wreck Diving
- Wrecks
- Yap
Archives
- January 2024
- April 2023
- March 2020
- March 2019
- January 2019
- November 2018
- September 2018
- July 2018
- May 2018
- March 2018
- January 2018
- October 2017
- September 2017
- June 2017
- April 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- October 2016
- August 2016
- July 2016
- May 2016
- March 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- December 2015
- August 2015
- June 2015
- April 2015
- January 2015
- November 2014
- July 2014
- April 2014
- February 2014
- December 2013
- November 2013
- October 2013
- September 2013
- August 2013
- July 2013
- June 2013
- May 2013
- April 2013
- March 2013
- February 2013
- January 2013
- December 2012
- November 2012
- October 2012
- September 2012
- August 2012
- July 2012
- June 2012
- May 2012
- April 2012












